Lambert's Cosine Law
Lambert's Cosine Law states that the apparent brightness of a diffuse reflecting surface is directly proportional to the cosine of the angle between the surface normal and the viewing direction. This relationship is fundamental to understanding how light interacts with matte surfaces.
The formula is simple but powerful:
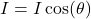
Where:
- I is the observed intensity
- I₀ is the maximum intensity (when the surface faces the light directly)
- θ (theta) is the angle between the surface normal and the light direction
This relationship explains why surfaces appear darker as they tilt away from the light source, forming the basis for diffuse reflection calculations in computer graphics and lighting design.
Try adjusting the surface angle in the interactive demo above to see how the brightness changes according to Lambert's Cosine Law. Notice how the brightness falls off gradually as the angle increases, reaching zero at 90 degrees.